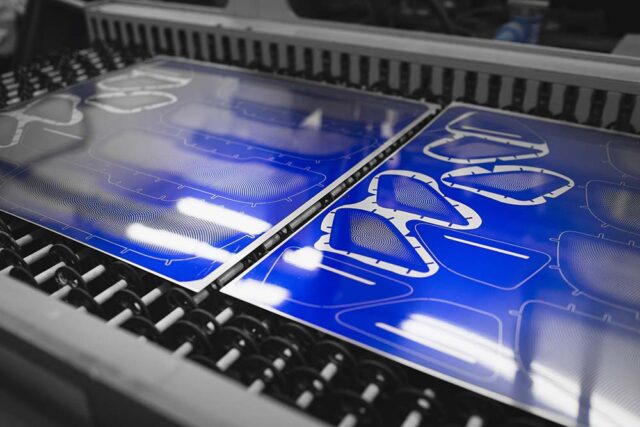
Chemical etching is an inscribing technique that involves eliminating substances with a chemical spray that is high in temperature and pressure to build a lasting engraved picture in metal. In order to develop the required image, a gloss or resist is put to the substance’s surface. Later, it is eliminated, uncovering the metal.
By warming the solution and sprinkling it at elevated pressure, the etching device accelerates the corrosion response between the chemical and the substance. This chemical mist disperses exposed metal regions, allowing the substance to be engraved slowly for a burr-free texture.
There are many metals that can be etched if you use the right etchant and devices. For instance, those metals include brass, stainless steel, bronze, titanium, zinc, gold, silver, copper, aluminum, molybdenum, nitinol, magnesium, beryllium copper, nickel, nickel silver, Inconel, mu-metal, and phosphor bronze, and many more.
Page Contents
Explaining How Chemical Etching Works
Computer-aided layout tools and photos are necessary for photo chemical etching procedures. Clients have to submit a sketch, which will be transformed into a picture tool by skilled experts. Since tweaks and redesigns can be made promptly, this technique is affordable.
After choosing the metal type, it is sliced into delicate sheets, rinsed, and ready for engraving. A coating system is used to apply a photosensitive substance or photoresist to the sheet. The photoresist is sensitive to light and shows resistance to acid.
A renewable plotter film contains all the features of components, allowing the identical part to be manufactured as many times as necessary. In addition to that, large volumes can be generated at a lower cost.
The metal sheet is positioned in between double sheets of photographic film and uncovered to UV radiation on either side. The endangered resist gets harder, whereas the dark regions stay smooth. During expansion, the softer resist is rinsed away, which evacuates the uncovered substance for the heated etchant to disperse.
In order to manufacture the necessary components, the solid resist will safeguard the intended substance from the etchant. The photoresist is removed after the chemicals are added. Also, the metal components are examined to guarantee that they suit the client’s specifications.
Step By Step Chemical Etching Process
Here are the basic steps that are involved in the chemical etching process.
Cleaning:
This procedure entails cleaning the surface of the metal that will be engraved of oils, grease, debris, and other impurities. Cleaning is critical since a dirty surface might cause the photoresist coating to adhere poorly, resulting in flaws. Staff should avoid touching the substance with their hands after finishing this procedure since oils and sweat from our skin can pollute it.
Lamination:
In this step, the dry film photoresist is applied to the surface. The components of the metal that will not be engraved are preserved with a photoresist. These films are added to either side of the substance utilizing temperature, pressure, and, in specific cases, water.
Exposure:
The substance is directed between two masks that contain the adverse picture of the component to be manufactured in this stage. The masks are constructed of glass or mylar. After that, high-intensity UV light is shone on the masks in both directions, which crosslinks the film in areas where the mask pictures do not obstruct the light.
Developing:
The substance has to be formulated after exposure. The non-crosslinked coating is chemically dispersed in this stage, revealing the bare metal under it. The film-protected material will eventually become the complete item.
Etching:
Following the development, the metal is grazed into etching halls where etchant is sprinkled at the same time from the upside and downside. In order to get the required output, this technique etches or disperses the uncoated metal. An etchant bath needs comprehensive observation of the attention, configuration, temperature, and duration in the etchant.
Stripping:
In the stripping procedure, the film is eliminated from the etched item with the help of another chemistry concentration.
Cleaning and Drying:
In this final phase, the item is detailed, and the films are omitted. It is better to wash it reasonably to peel off all residuals. It is conducted with the help of deionized water and reverse osmosis water.
What Are The Advantages Of Chemical Etching

Here we have listed the benefits of chemical itching you need to know about.
1. Detailed Tooling
The photo chemical etching tooling is not difficult. It is a highly accurate, affordable, and CAD-produced digital tooling.
2. Danger-free Layout
With this process, it is possible to generate prototypes in relatively quick lead times. In addition, the complexness of the layout is not a problem.
3. No Changes
No heat or mechanical force is used in the chemical etching procedure. It implies that the properties of the metal will not change. The substance’s temper will not vary, and components are free from the burr.
4. Does Not Need Finishing
The final net pattern machining lessens the necessity for conventional finishing. Also, the metal etching procedure does not leave any jagged burrs or edges.
5. Several Thicknesses And Tolerances
It is possible to etch several substances and thicknesses ranging from 0.005 mm to 2.5 mm. When part features are carved, the possible component complexness is nearly infinite with the precision of ±0.025 mm.
What Are The Applications Of Chemical Etching
Here are the most common applications of chemical etching.
In the sign field, chemical etching is utilized to create premium-quality, long-lasting items like labels, nameplates, monument objects, elevator doors, medals, and trophies.
Etching is also utilized to make a broad range of items in the electronics sector, such as printed circuit boards, metal foil distress measures, stencils, filters, shims, and washers.
Chemical etching is employed in the printing field to provide the best quality, reliable goods like hot foil stamping dies, adaptable cutting dies, intaglio printing, and embossing cylinders.
Bottom Line
As you can see, we have mentioned about the photo chemical etching and how it will work. Also, plenty of metals and metal alloys can be etched with this cost-effective process.