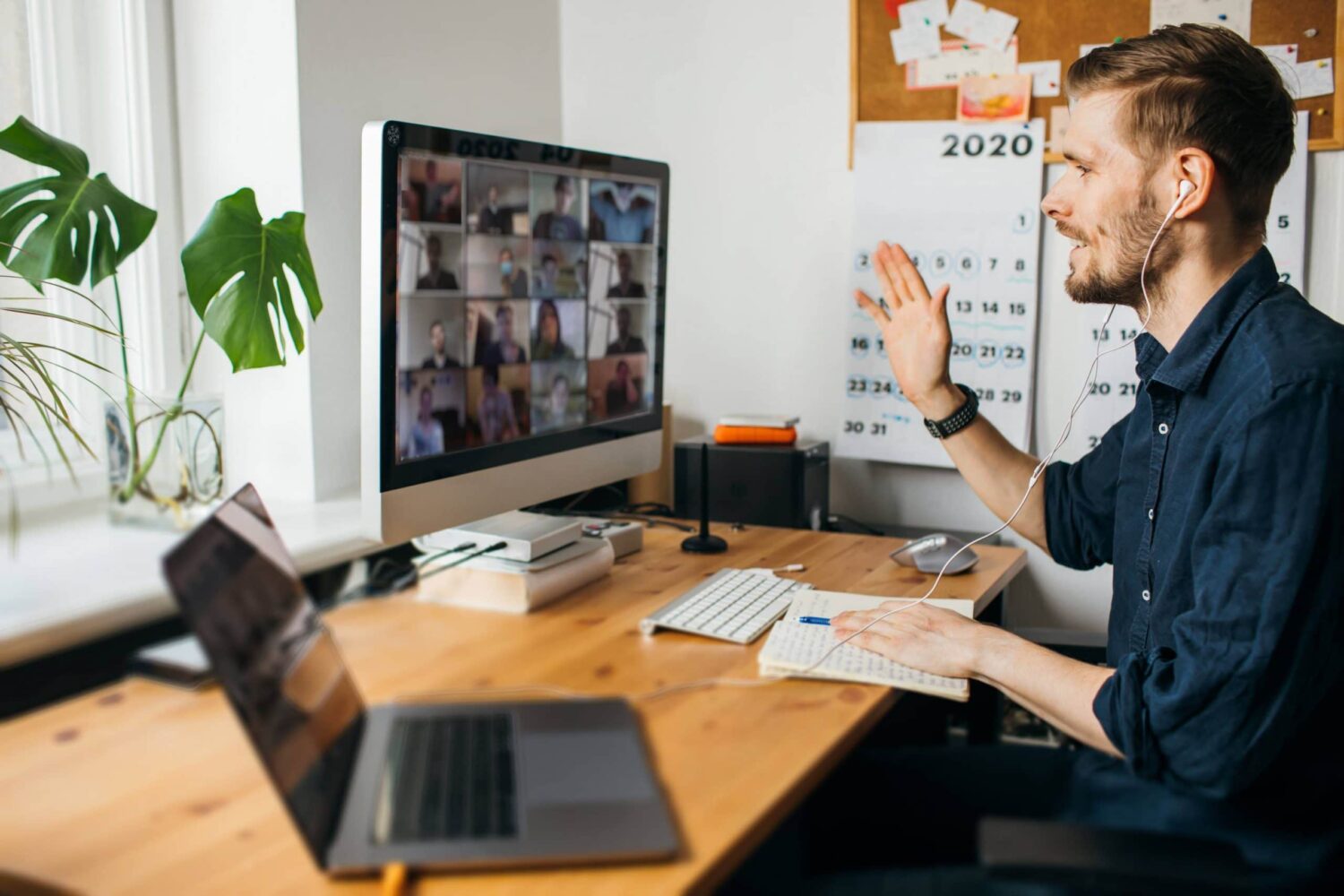
As remote working has become the norm for many organizations, IT support for those employees is of great importance. With an increasingly mobile workforce, IT teams need to be prepared and equipped with the tools necessary to provide technical assistance in a timely manner.
This article explores the challenges that come along with providing IT support remotely, as well as potential solutions that can help make sure businesses are running smoothly and securely.
From streamlining communications between departments to maintaining secure systems and data access, this article will discuss key strategies for successful remote worker IT support.
Page Contents
Challenges of Supporting Remote IT Workers
Supporting remote IT workers can be a major challenge for any organization. Despite the potential cost savings and increased productivity, managing a distributed workforce comes with its own unique set of difficulties. One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that the necessary IT support services are available to employees working from home or other offsite locations.
This requires providing reliable access to applications, software updates and security protocols in addition to general technical assistance when needed. Additionally, businesses must account for differing levels of knowledge among their remote staff when it comes to utilizing technology; some may require more guidance on how to use certain tools while others need troubleshooting advice if they experience connection issues or hardware problems.
Finally, organizations have to maintain consistent communication with their remote workers so that all parties remain up-to-date regarding any changes within the company’s IT system. By understanding these key challenges and implementing comprehensive solutions, businesses can successfully manage an effective remote work environment without compromising employee satisfaction or productivity levels.
Strategies for Mitigating Remote Worker IT Issues
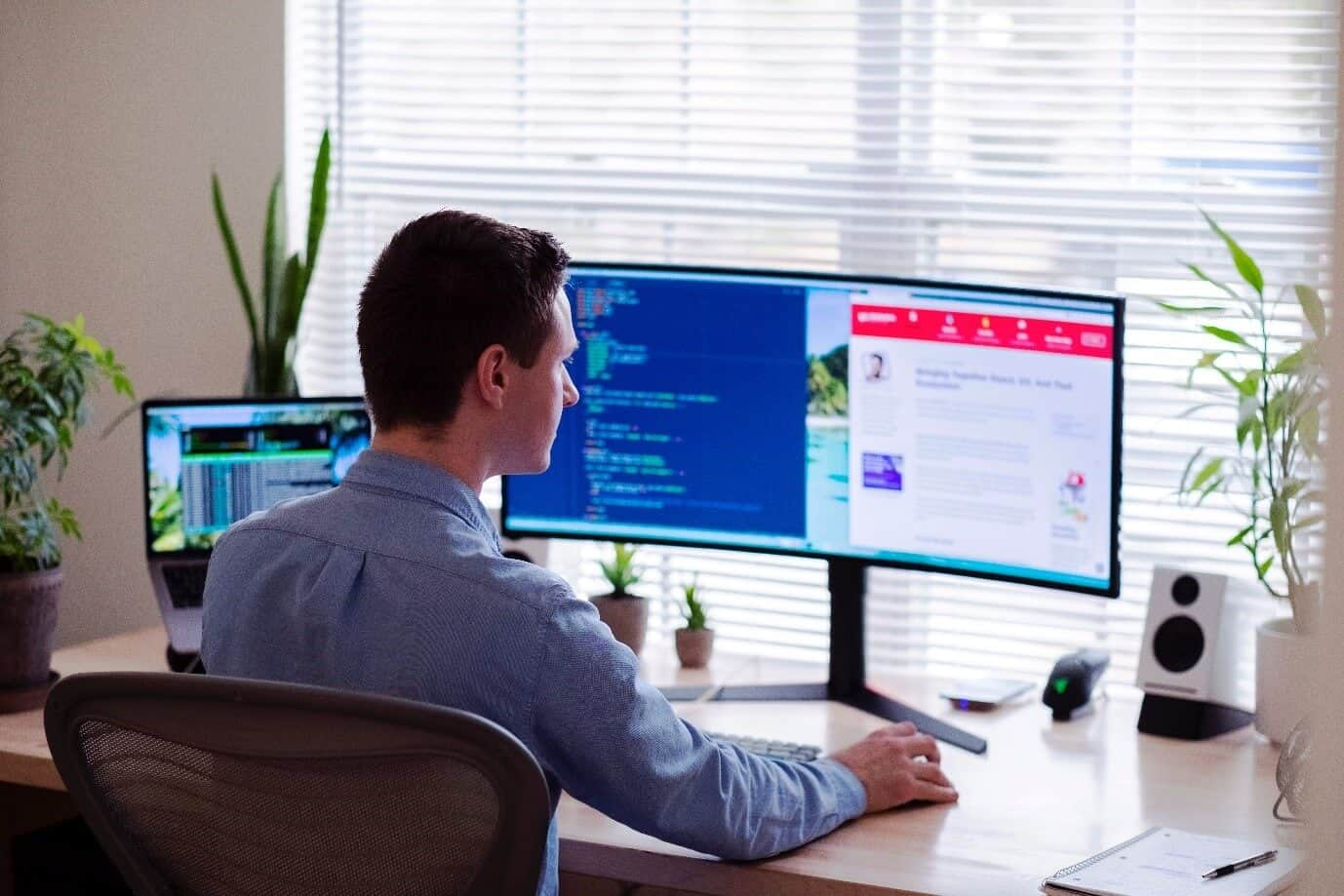

When supporting remote workers, IT departments must find ways to mitigate problems quickly and efficiently. One of the most effective strategies for doing so is to ensure that employees are properly trained on how to use the necessary tools and resources in order to best support themselves. This should include providing them with clear instructions on how to set up their home office, as well as troubleshooting advice when needed.
Additionally, employers should make sure that their IT infrastructure is secure by implementing policies such as two-factor authentication, encrypted data transfer protocols, and regular software updates. Advanced monitoring solutions can also be used to track employee activities across any device they use while working remotely so that any potential security threats can be identified early on before they become a major problem.
Finally, it’s important for employers to have a reliable support system in place; this could involve having dedicated customer service staff available 24/7 or setting up an online forum where employees can ask questions and receive immediate answers from experts within the organization. By making these investments now, organizations will save time and money in the long run by reducing costly downtime due to technical issues caused by remote workers.
Solutions for Enhancing Remote Worker Productivity and Efficiency
To maximize productivity and efficiency for remote workers, IT teams must implement solutions that are tailored to the unique challenges of a distributed workforce. One way to do this is by providing robust software tools that make it easy for remote team members to collaborate remotely in real-time.
Video conferencing software such as Zoom or Google Hangouts can be used to facilitate virtual meetings while document sharing programs like Dropbox can ensure everyone has access to the same information regardless of their physical location. Additionally, cloud storage systems should be implemented so employees have access to important files and documents without having to rely on email attachments or USB drives.
Another solution for enhancing remote worker productivity and efficiency is making sure all employees have reliable Internet connections with enough bandwidth available for video conferencing, file transfers, and other online tasks. Without an adequate connection speed, tasks will take longer than necessary which leads directly into lower overall productivity levels across the board.
Moreover, IT teams should also provide training materials so employees understand how best use the various tools they’re given as well as offer technical support when needed since any delays caused due from technical issues could further reduce individual employee performance levels. Finally, creating clear communication protocols between managers and employees is essential in order maintain high standards of performance even when working remotely.
This includes setting expectations regarding check-in times each day or establishing certain deadlines prioritizes urgent tasks over less pressing ones – all while keeping lines of communication open at all times throughout workdays regardless if everyone is scattered around different locations
Best Practices for Troubleshooting Common Issues with Remote Workers
When it comes to troubleshooting common issues with remote workers, IT support teams must take into account the unique challenges posed by distributed workforces. One of the best practices for ensuring successful troubleshooting is to have a clear communication strategy in place from the outset.
This includes defining expectations and procedures for how problems should be reported and addressed, as well as what types of responses and updates can be expected from IT support staff.
Establishing an open line of communication between remote workers and IT departments helps ensure that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities on both sides before any issue arises. Additionally, having regular check-ins with members of the team allows IT personnel to stay informed about potential problems or changes in workflow that could lead to technical errors down the road.
Finally, investing in proactive monitoring tools can provide valuable metrics regarding system usage patterns which can help identify issues before they become serious enough to cause disruption or require more advanced corrective techniques.
Security Considerations When Supporting a Distributed Workforce
When it comes to supporting a distributed workforce, security is a major concern for IT teams. Remote workers need access to the same data and applications as their in-office counterparts, but without putting confidential company information at risk of being compromised or stolen.
Fortunately, there are steps that can be taken to ensure remote employees remain secure while working from home. The first step is implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) when granting access to sensitive systems and data. MFA requires users to provide additional credentials beyond just username and password, such as an email address or mobile phone number.
This adds another layer of protection against unauthorized access attempts by malicious actors trying to gain entry into the system. Additionally, IT personnel should consider restricting user access rights based on job roles so that only necessary individuals can view certain types of data or applications within the network. Another important factor in protecting remote workers is ensuring they have reliable antivirus software installed on their computers with regular updates applied as soon as possible after release date.
Since many organizations rely heavily on hosted cloud services like Microsoft Office 365 and Google G-Suite for collaborative workflows, it’s also vital that these services are kept up-to-date with proper security measures enabled during the setup phase (such as two-factor authentication). Last but not least, having robust backup solutions in place will ensure that even if something does go wrong all key documents and files can quickly be recovered without any disruption in workflow or business continuity planning efforts.