Rodents such as mice and rats scurrying through your home floors and walls are more than an annoyance. The risk they pose does more than the irreversible damage caused when they gnaw on your belongings and building materials.
The accumulation of feces from these uninvited guests can contaminate food and food surfaces, trigger allergic reactions in humans, and spread bacteria. Once the fecal matter becomes dry, it can be dangerous to those who breathe in it.
Furthermore, rodent droppings can pose a severe health risk to humans through the various illness-causing parasites and microbes they can carry.
Page Contents
7 Common illnesses transmitted to humans by rodents
1. Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome
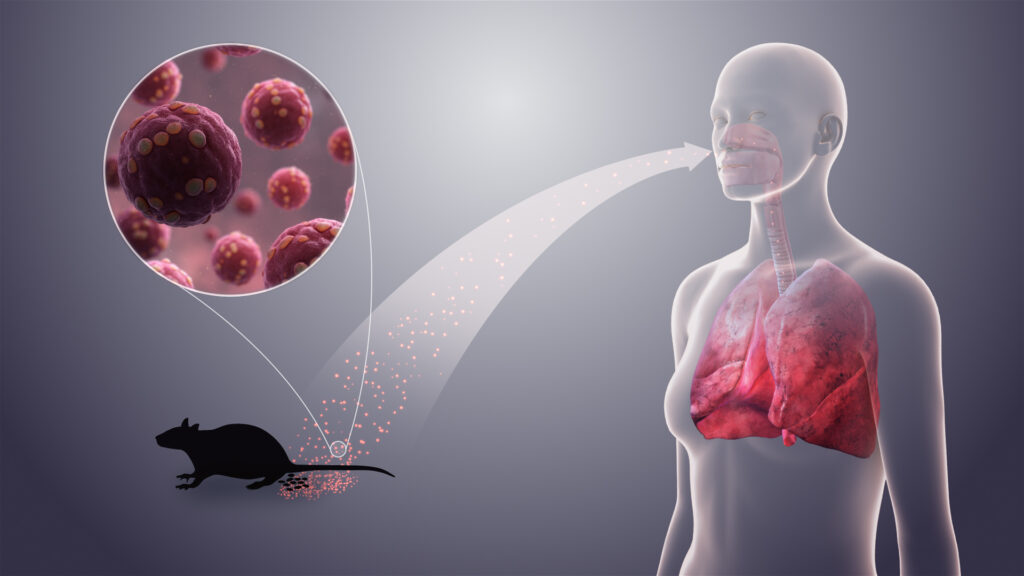
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) is the illness that often comes to mind when individuals refer to hazards inherent to different rodent species, particularly the deer mice. Since the illness was discovered back in 1993, there have been over 500 reported deaths connected to it.
One element of danger is that you don’t have to touch or even be bitten by a rodent to contract the illness since the virus is found in the urine and feces of rodents and can also be inhaled. And so, you should consider wearing a protective mask when cleaning up any area, which contains rodent droppings.
Luckily, the illness is very rare, but it receives a lot of publicity because of its severity.
2. Plaque
Plaque is a bacterial infection that is spread primarily by fleas. Yersinia pestis, the organism that causes it, lives in rodents mostly found in semirural and rural areas. The organism is spread to humans bitten by rodent fleas, which have fed on infected fleas.
Referred to as the “Black Death” back in the 1300s, today, this highly contagious illness occurs in fewer than five thousand individuals a year in the world. Plaque can be fatal if not treated, meaning that it’s still a threat that shouldn’t be taken lightly.
The common form of plaque leads to tender and swollen lymph nodes in the groin, neck, or armpits. The deadliest and rarest form of plaque usually affects the lungs, and it’s contagious.
3. Rat-Bite fever
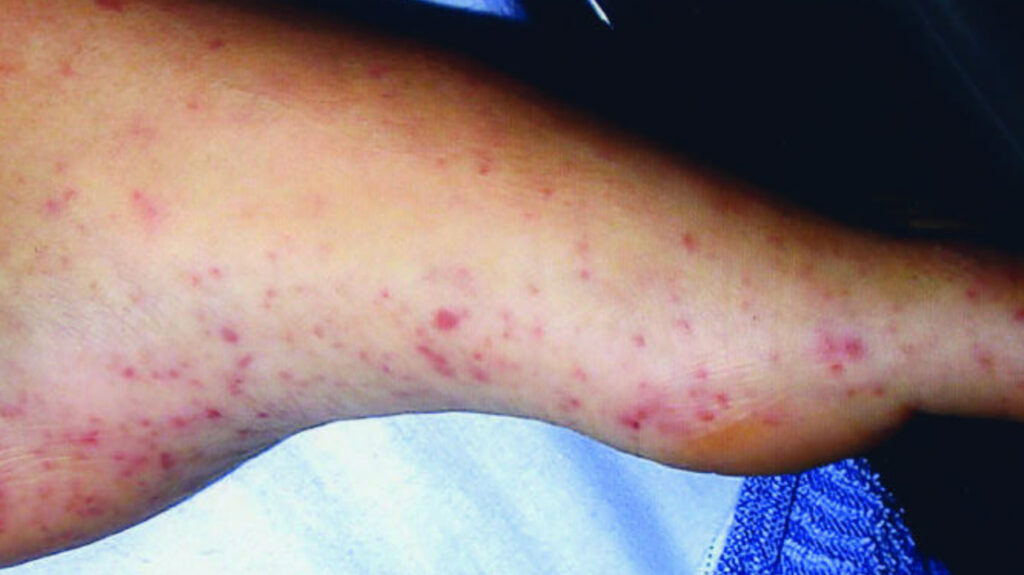
Mice and rats may carry and transmit the bacterium causing RBF, rat-bite fever. Humans can contract this deadly disease by handling rodents with the illness or consuming liquids or food that infected rodents have contaminated with this bacterium.
Rat-bite fever obtained by ingesting contaminated water or food is known as Haverhill fever, and the symptoms include joint pain, vomiting, and fever. Some of the serious diseases associated with RBF may include infections of the brain, lungs, heart, and abscesses or sores in the internal organs. It is normally treated with antibiotics; however, if not treated, it can kill.
4. Salmonellosis
This is a common foodborne disease. It can be spread in several different ways, such as mice and rats contaminating water and food with feces containing salmonella bacteria. Any direct contact or exposure with an infected rodent or an animal carrying the bacteria can cause salmonellosis as well.
This disease’s symptoms are sometimes very mild, as the bacteria is found in animal’s intestinal systems. But a severe infection can cause headache, blood in the feces, chills, fever, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, vomiting, and nausea.
5. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis (LCM)
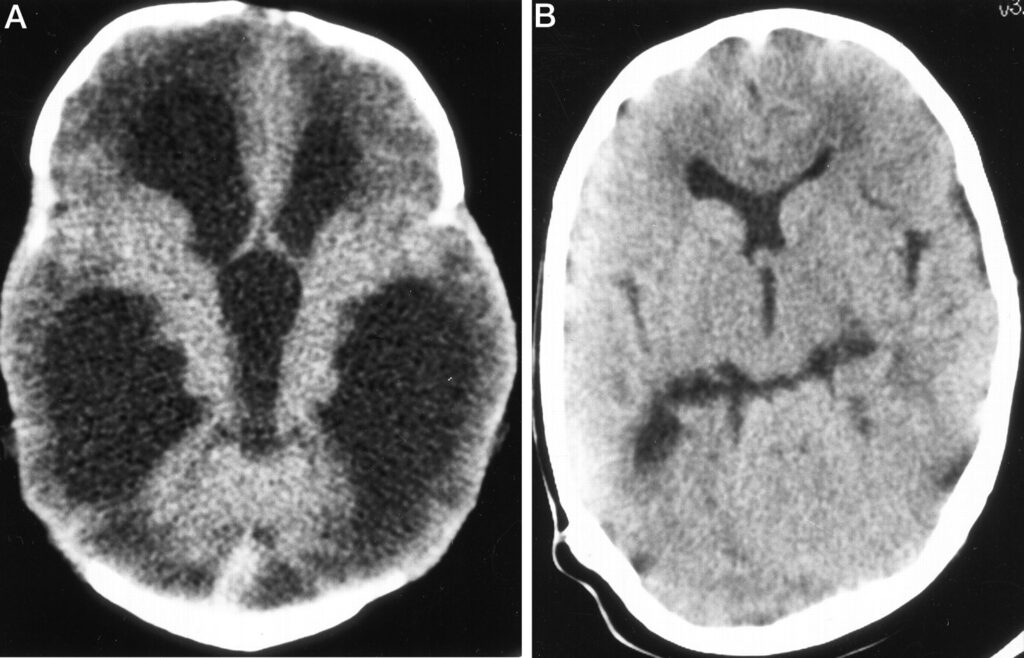
Another illness that needs to be mentioned is LCM, lymphocytic choriomeningitis. It is a common viral infection illness from common house mice and is caused by LCMV (lymphocytic choriomeningitis).
People can get infected by this virus after exposure to urine, saliva, droppings, and nesting materials of an infected rodent. Direct contact and bites through broken skin can cause an infection as well.
About 5% of common house mice normally carry the virus, but other domestic rodents like hamsters and guinea pigs can become carriers because of being infected by disease-carrying wild mice.
Symptoms of an infection are most commonly lack of appetite and mild fever, followed by vomiting, muscle aches, and headaches. Some patients also report having salivary gland pain, chest pain, and sore throat. In the second s
tage, LCM may cause meningitis and encephalitis.
6. Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a rare bacterial infection passed by rodents and other domestic and wild species. While the infected rodents are unaffected by Leptospira interrogans, it can cause serious issues to people who become infected.
You can get infected with the illness by:
• Touching mucous membranes or skin with soil or water that has been contaminated with the droppings of infected rodents.
• Drinking or eating food contaminated with droppings from infected rodents.
In most cases, the illness isn’t life-threatening, and symptoms resemble a case of flu. However, serious cases may even progress to meningitis, which is inflammation of the spinal tissues and brain. It can also cause kidney and liver failure.
7. Tularemia
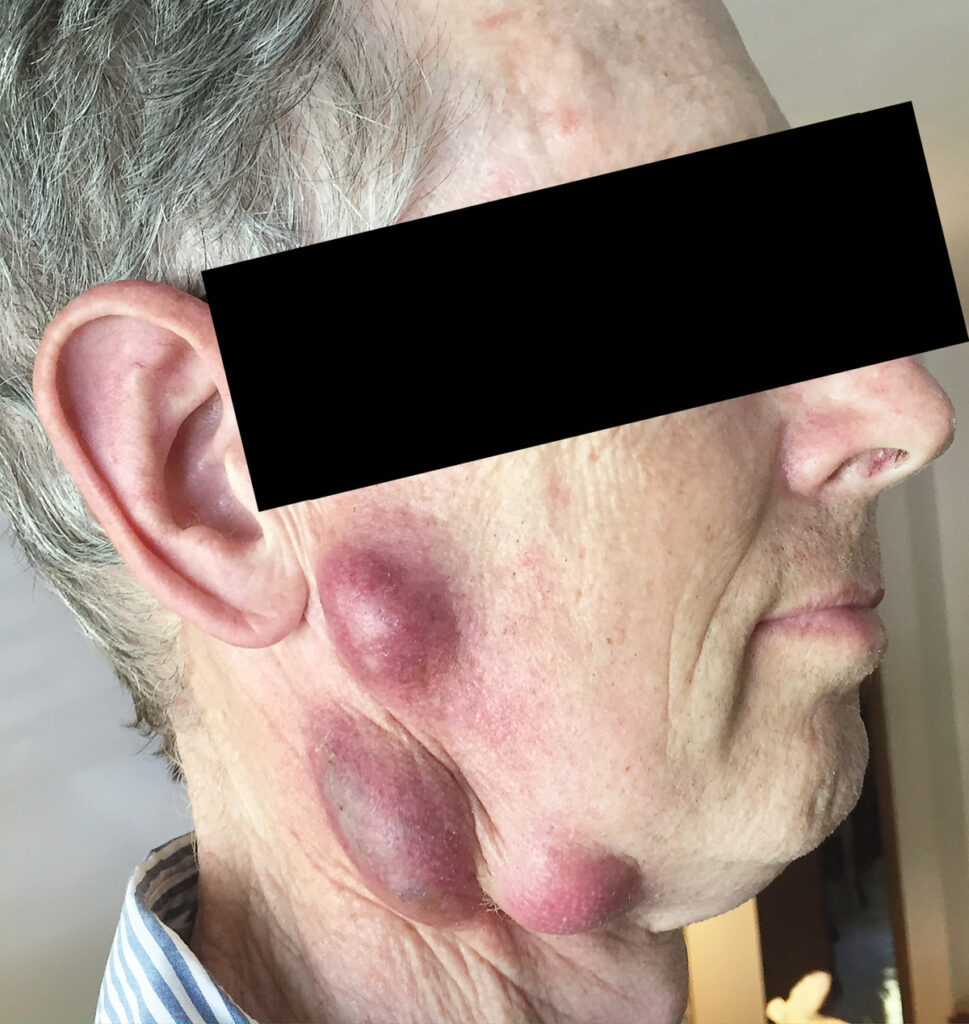
Tularemia, also known as Rabbit Fever, is an illness caused by the bacterium Francisella tularaemia. It is carried and transmitted by wild rodents, including beavers, ground squirrels, muskrats, etc.
When acquired through ingesting contaminated liquids and food, rabbit fever may cause lung infection, cough, or glandular swelling. The symptoms typically range from mild to real life-threatening, but most cases can be quickly treated using antibiotics.
How to get rid of rodents
To avoid salmonella and other illnesses caused by rodents and minimize the structural damage they can cause, you’ve to take steps to remove them from your house. Dead rodents and nest materials must be removed from your house. Always wear protective gloves when handling rodent droppings and dead rodents, and purchase a respirator with cartridges in order to avoid breathing in contaminants.
Also, keep in mind that rodents travel in packs. So if you’ve seen one in your house, it’s much likely that a family of rodents is still hiding. And if that is not enough, these creatures reproduce quickly. If there are signs of an infestation, it’s better to hire a professional pest control company like Excel Pest Services. The risk of illness is also high if you don’t know how to eliminate rodents properly.